open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s based on the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds
Linus Benedict Torvalds ( , ; born 28 December 1969) is a Finnish software engineer who is the creator and lead developer of the Linux kernel. He also created the distributed version control system Git.
He was honored, along with Shinya Yam ...
. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is oft ...
(distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
and released under the copyleft
Copyleft is the legal technique of granting certain freedoms over copies of copyrighted works with the requirement that the same rights be preserved in derivative works. In this sense, ''freedoms'' refers to the use of the work for any purpose, ...
GPL license.
Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint
Linux Mint is a community-developed Linux distribution. It is based on Ubuntu and designed for x86-64 based computers; another variant is based on Debian which is named Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE) and has both 64-bit and IA-32 support. T ...
, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu
Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed primarily of free and open-source software. Developed by the British company Canonical (company), Canonical and a community of contributors under a Meritocracy, meritocratic gover ...
, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985. The organisation supports the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed ...
uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy. Other than the Linux kernel, key components that make up a distribution may include a display server (windowing system), a package manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner.
A package manager deals wi ...
, a bootloader and a Unix shell
A Unix shell is a Command-line_interface#Command-line_interpreter, command-line interpreter or shell (computing), shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command languag ...
.
Linux is one of the most prominent examples of free and open-source software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
collaboration. While originally developed for x86 based personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s, it has since been ported to more platforms than any other operating system, and is used on a wide variety of devices including PCs, workstations, mainframes and embedded system
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is e ...
s. Linux is the predominant operating system for servers and is also used on all of the world's 500 fastest supercomputers. When combined with Android, which is Linux-based and designed for smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s, they have the largest installed base of all general-purpose operating systems.
Overview
The Linux kernel was designed byLinus Torvalds
Linus Benedict Torvalds ( , ; born 28 December 1969) is a Finnish software engineer who is the creator and lead developer of the Linux kernel. He also created the distributed version control system Git.
He was honored, along with Shinya Yam ...
, following the lack of a working kernel for GNU, a Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
-compatible operating system made entirely of free software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
that had been undergoing development since 1983 by Richard Stallman
Richard Matthew Stallman ( ; born March 16, 1953), also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to ...
. A working Unix system called Minix was later released but its license was not entirely free at the time and it was made for an educative purpose. The first entirely free Unix for personal computers, 386BSD, did not appear until 1992, by which time Torvalds had already built and publicly released the first version of the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
on the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
. Like GNU and 386BSD, Linux did not have any Unix code, being a fresh reimplementation, and therefore avoided the then legal issues. Linux distributions became popular in the 1990s and effectively made Unix technologies accessible to home users on personal computers whereas previously it had been confined to sophisticated workstations.
Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland and a desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphi ...
such as GNOME, KDE Plasma
KDE Plasma is a Shell (computing), graphical shell developed by the KDE community for Unix-like operating systems. It serves as the interface layer between the user and the operating system, providing a graphical user interface (GUI) and workspa ...
or Xfce. Distributions intended for servers may not have a graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
at all or include a solution stack such as LAMP.
The source code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
of Linux may be used, modified, and distributed commercially or non-commercially by anyone under the terms of its respective licenses, such as the GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first ...
(GPL). The license means creating novel distributions is permitted by anyone and is easier than it would be for an operating system such as MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
or Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
. The Linux kernel, for example, is licensed under the GPLv2, with an exception for system call
In computing, a system call (syscall) is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services (for example, accessing a hard disk drive ...
s that allows code that calls the kernel via system calls not to be licensed under the GPL.
Because of the dominance of Linux-based Android on smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s, Linux, including Android, has the largest installed base of all general-purpose operating systems . Linux is, , used by around 4 percent of desktop computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuratio ...
s. The Chromebook
Chromebook (sometimes stylized in lowercase as chromebook) is a line of laptops, desktops, tablets and all-in-one computers that run ChromeOS, a proprietary operating system developed by Google.
Chromebooks are optimised for web access. They al ...
, which runs the Linux kernel-based ChromeOS, dominates the US K–12 education market and represents nearly 20 percent of sub-$300 notebook
A notebook (also known as a notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, or legal pad) is a book or stack of paper pages that are often ruled and used for purposes such as note-taking, journaling or other writing, drawing, or scrapbooking and more.
...
sales in the US. Linux is the leading operating system on servers (over 96.4% of the top one million web servers' operating systems are Linux), leads other big iron systems such as mainframe computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise ...
s, and is used on all of the world's 500 fastest supercomputers (, having gradually displaced all competitors).
Linux also runs on embedded system
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is e ...
s, i.e., devices whose operating system is typically built into the firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
and is highly tailored to the system. This includes routers, automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
controls, smart home devices, video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s, television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
s (Samsung and LG smart TVs), automobiles
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
(Tesla, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, Hyundai, and Toyota), and spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
(Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
rocket, Dragon
A dragon is a Magic (supernatural), magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but European dragon, dragons in Western cultures since the Hi ...
crew capsule, and the Ingenuity Mars helicopter).
History
Precursors
TheUnix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
operating system was conceived of and implemented in 1969, at AT&T
AT&T Inc., an abbreviation for its predecessor's former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the w ...
's Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
in the United States, by Ken Thompson
Kenneth Lane Thompson (born February 4, 1943) is an American pioneer of computer science. Thompson worked at Bell Labs for most of his career where he designed and implemented the original Unix operating system. He also invented the B (programmi ...
, Dennis Ritchie, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna
Joseph Frank Ossanna, Jr. (December 10, 1928 – November 28, 1977) was an American electrical engineer and computer programmer who worked as a member of the technical staff at the Bell Labs, Bell Telephone Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jer ...
. First released in 1971, Unix was written entirely in assembly language
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence bet ...
, as was common practice at the time. In 1973, in a key pioneering approach, it was rewritten in the C programming language by Dennis Ritchie (except for some hardware and I/O routines). The availability of a high-level language implementation of Unix made its porting to different computer platforms easier.
As a 1956 antitrust case forbade AT&T from entering the computer business, AT&T provided the operating system's source code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
to anyone who asked. As a result, Unix use grew quickly and it became widely adopted by academic institution
An academic institution is an educational institution dedicated to education and research, which grants academic degrees. See also academy and university.
Types
* Primary schools – (from French ''école primaire'') institutions where childre ...
s and businesses. In 1984, AT&T divested itself of its regional operating companies, and was released from its obligation not to enter the computer business; freed of that obligation, Bell Labs began selling Unix as a proprietary product, where users were not legally allowed to modify it.
Onyx Systems began selling early microcomputer-based Unix workstations in 1980. Later, Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
, founded as a spin-off of a student project at Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
, also began selling Unix-based desktop workstations in 1982. While Sun workstations did not use commodity PC hardware, for which Linux was later originally developed, it represented the first successful commercial attempt at distributing a primarily single-user microcomputer that ran a Unix operating system.
With Unix increasingly "locked in" as a proprietary product, the GNU Project
The GNU Project ( ) is a free software, mass collaboration project announced by Richard Stallman on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and Computer hardware, computing dev ...
, started in 1983 by Richard Stallman
Richard Matthew Stallman ( ; born March 16, 1953), also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to ...
, had the goal of creating a "complete Unix-compatible software system" composed entirely of free software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
. Work began in 1984. Later, in 1985, Stallman started the Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985. The organisation supports the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed ...
and wrote the GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first ...
(GNU GPL) in 1989. By the early 1990s, many of the programs required in an operating system (such as libraries, compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
s, text editor
A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. An example of such program is "notepad" software (e.g. Windows Notepad). Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to c ...
s, a command-line shell, and a windowing system) were completed, although low-level elements such as device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s, daemons, and the kernel, called GNU Hurd, were stalled and incomplete.
Minix was created by Andrew S. Tanenbaum, a computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
professor, and released in 1987 as a minimal Unix-like operating system targeted at students and others who wanted to learn operating system principles. Although the complete source code of Minix was freely available, the licensing terms prevented it from being free software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
until the licensing changed in April 2000.
Creation
While attending theUniversity of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki (, ; UH) is a public university in Helsinki, Finland. The university was founded in Turku in 1640 as the Royal Academy of Åbo under the Swedish Empire, and moved to Helsinki in 1828 under the sponsorship of Alexander ...
in the fall of 1990, Torvalds enrolled in a Unix course. The course used a MicroVAX
The MicroVAX is a discontinued family of low-cost minicomputers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). The first model, the MicroVAX I, shipped in 1984. The series uses processors that implement the VAX instruction se ...
minicomputer running Ultrix, and one of the required texts was '' Operating Systems: Design and Implementation'' by Andrew S. Tanenbaum. This textbook included a copy of Tanenbaum's Minix operating system. It was with this course that Torvalds first became exposed to Unix. In 1991, he became curious about operating systems. Frustrated by the licensing of Minix, which at the time limited it to educational use only, he began to work on his operating system kernel, which eventually became the Linux kernel.
On July 3, 1991, to implement Unix system call
In computing, a system call (syscall) is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services (for example, accessing a hard disk drive ...
s, Linus Torvalds attempted unsuccessfully to obtain a digital copy of the POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX; ) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines application programming interfaces (APIs), along with comm ...
standards documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge managem ...
with a request to the ''comp.os.minix'' newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start ...
. After not finding the POSIX documentation, Torvalds initially resorted to determining system calls from SunOS
SunOS is a Unix-branded operating system developed by Sun Microsystems for their workstation and server computer systems from 1982 until the mid-1990s. The ''SunOS'' name is usually only used to refer to versions 1.0 to 4.1.4, which were based ...
documentation owned by the university for use in operating its Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
server. He also learned some system calls from Tanenbaum's Minix text.
Torvalds began the development of the Linux kernel on Minix and applications written for Minix were also used on Linux. Later, Linux matured and further Linux kernel development took place on Linux systems. GNU applications also replaced all Minix components, because it was advantageous to use the freely available code from the GNU Project with the fledgling operating system; code licensed under the GNU GPL can be reused in other computer programs as long as they also are released under the same or a compatible license. Torvalds initiated a switch from his original license, which prohibited commercial redistribution, to the GNU GPL. Developers worked to integrate GNU components with the Linux kernel, creating a fully functional and free operating system.
Although not released until 1992, due to legal complications, the development of 386BSD, from which NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
, OpenBSD and FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
descended, predated that of Linux. Linus Torvalds has stated that if the GNU kernel or 386BSD had been available in 1991, he probably would not have created Linux.
Naming
 Linus Torvalds had wanted to call his invention "Freax", a
Linus Torvalds had wanted to call his invention "Freax", a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
of "free", "freak", and "x" (as an allusion to Unix). During the start of his work on the system, some of the project's makefile
In software development, Make is a command-line interface software tool that performs actions ordered by configured Dependence analysis, dependencies as defined in a configuration file called a ''makefile''. It is commonly used for build automati ...
s included the name "Freax" for about half a year. Torvalds considered the name "Linux" but dismissed it as too egotistical.Torvalds, Linus and Diamond, David, ''Just for Fun: The Story of an Accidental Revolutionary'', 2001,
To facilitate development, the files were uploaded to the FTP server of FUNET in September 1991. Ari Lemmke, Torvalds' coworker at the Helsinki University of Technology (HUT) who was one of the volunteer administrators for the FTP server at the time, did not think that "Freax" was a good name, so he named the project "Linux" on the server without consulting Torvalds. Later, however, Torvalds consented to "Linux".
According to a newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start ...
post by Torvalds, the word "Linux" should be pronounced ( ) with a short 'i' as in 'print' and 'u' as in 'put'. To further demonstrate how the word "Linux" should be pronounced, he included an audio guide with the kernel source code. However, in this recording, he pronounces Linux as ' () with a short but close front unrounded vowel, instead of a near-close near-front unrounded vowel
The near-close near-front unrounded vowel, or near-high near-front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , the small capital ...
as in his newsgroup post.
Commercial and popular uptake
The adoption of Linux in production environments, rather than being used only by hobbyists, started to take off first in the mid-1990s in the supercomputing community, where organizations such asNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
started to replace their increasingly expensive machines with clusters of inexpensive commodity computers running Linux. Commercial use began when Dell
Dell Inc. is an American technology company that develops, sells, repairs, and supports personal computers (PCs), Server (computing), servers, data storage devices, network switches, software, computer peripherals including printers and webcam ...
and IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
, followed by Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
, started offering Linux support to escape Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
's monopoly in the desktop operating system market.
Today, Linux systems are used throughout computing, from embedded system
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is e ...
s to virtually all supercomputer
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instruc ...
s, and have secured a place in server installations such as the popular LAMP application stack. The use of Linux distributions in home and enterprise desktops has been growing.
Linux distributions have also become popular in the netbook market, with many devices shipping with customized Linux distributions installed, and Google releasing their own ChromeOS designed for netbooks.
Linux's greatest success in the consumer market is perhaps the mobile device market, with Android being the dominant operating system on smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s and very popular on tablets and, more recently, on wearables, and vehicles. Linux gaming is also on the rise with Valve showing its support for Linux and rolling out SteamOS, its own gaming-oriented Linux distribution, which was later implemented in their Steam Deck platform. Linux distributions have also gained popularity with various local and national governments, such as the federal government of Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
.
Development
Linus Torvalds is the lead maintainer for the Linux kernel and guides its development, while Greg Kroah-Hartman is the lead maintainer for the stable branch. Zoë Kooyman is the executive director of the Free Software Foundation, which in turn supports the GNU components. Finally, individuals and corporations develop third-party non-GNU components. These third-party components comprise a vast body of work and may include both kernel modules and user applications and libraries. Linux vendors and communities combine and distribute the kernel, GNU components, and non-GNU components, with additional package management software in the form of Linux distributions.Design
Many developers of open-source software agree that the Linux kernel was not designed but rather evolved throughnatural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
. Torvalds considers that although the design of Unix served as a scaffolding, "Linux grew with a lot of mutations – and because the mutations were less than random, they were faster and more directed than alpha-particles in DNA." Eric S. Raymond considers Linux's revolutionary aspects to be social, not technical: before Linux, complex software was designed carefully by small groups, but "Linux evolved in a completely different way. From nearly the beginning, it was rather casually hacked on by huge numbers of volunteers coordinating only through the Internet. Quality was maintained not by rigid standards or autocracy but by the naively simple strategy of releasing every week and getting feedback from hundreds of users within days, creating a sort of rapid Darwinian selection on the mutations introduced by developers." Bryan Cantrill, an engineer of a competing OS, agrees that "Linux wasn't designed, it evolved", but considers this to be a limitation, proposing that some features, especially those related to security, cannot be evolved into, "this is not a biological system at the end of the day, it's a software system."
A Linux-based system is a modular Unix-like operating system, deriving much of its basic design from principles established in Unix during the 1970s and 1980s. Such a system uses a monolithic kernel
A monolithic kernel is an operating system software architecture, architecture with the entire operating system running in kernel space. The monolithic model differs from other architectures such as the microkernel in that it alone defines a high ...
, the Linux kernel, which handles process control, networking, access to the peripheral
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
s, and file systems. Device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s are either integrated directly with the kernel or added as modules that are loaded while the system is running.
The GNU userland is a key part of most systems based on the Linux kernel, with Android being the notable exception. The GNU C library, an implementation of the C standard library
The C standard library, sometimes referred to as libc, is the standard library for the C (programming language), C programming language, as specified in the ISO C standard.International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrote ...
, works as a wrapper for the system calls of the Linux kernel necessary to the kernel-userspace interface, the toolchain
A toolchain is a set of software development tools used to build and otherwise develop software. Often, the tools are executed sequentially and form a pipeline such that the output of one tool is the input for the next. Sometimes the term is us ...
is a broad collection of programming tools vital to Linux development (including the compilers
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs tha ...
used to build the Linux kernel itself), and the coreutils implement many basic Unix tools. The GNU Project also develops Bash, a popular CLI shell. The graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
(or GUI) used by most Linux systems is built on top of an implementation of the X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
. More recently, some of the Linux community has sought to move to using Wayland as the display server protocol, replacing X11.
Many other open-source software projects contribute to Linux systems.
Installed components of a Linux system include the following:
* A bootloader, for example GNU GRUB, LILO, SYSLINUX or systemd-boot. This is a program that loads the Linux kernel into the computer's main memory
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processin ...
, by being executed by the computer when it is turned on and after the firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
initialization is performed.
* An init program, such as the traditional sysvinit and the newer systemd, OpenRC and Upstart. This is the first process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
launched by the Linux kernel, and is at the root of the process tree. It starts processes such as system services and login prompts (whether graphical or in terminal mode).
* Software libraries, which contain code that can be used by running processes. On Linux systems using ELF
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
-format executable files, the dynamic linker that manages the use of dynamic libraries is known as ld-linux.so. If the system is set up for the user to compile software themselves, header files will also be included to describe the programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build su ...
of installed libraries. Besides the most commonly used software library on Linux systems, the GNU C Library (glibc), there are numerous other libraries, such as SDL and Mesa.
** The C standard library
The C standard library, sometimes referred to as libc, is the standard library for the C (programming language), C programming language, as specified in the ISO C standard.International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrote ...
is the library necessary to run programs written in C on a computer system, with the GNU C Library being the standard. It provides an implementation of the POSIX API, as well as extensions to that API. For embedded systems, alternatives such as musl, EGLIBC (a glibc fork once used by Debian) and uClibc (which was designed for uClinux) have been developed, although the last two are no longer maintained. Android uses its own C library, Bionic. However, musl can additionally be used as a replacement for glibc on desktop and laptop systems, as seen on certain Linux distributions like Void Linux.
* Basic Unix commands, with GNU coreutils being the standard implementation. Alternatives exist for embedded systems, such as the copyleft BusyBox, and the BSD-licensed Toybox.
* Widget toolkit
A widget toolkit, widget library, GUI toolkit, or UX library is a library (computing), library or a collection of libraries containing a set of graphical control elements (called ''widgets'') used to construct the graphical user interface (GUI) of ...
s are the libraries used to build graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
s (GUIs) for software applications. Numerous widget toolkits are available, including GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
and Clutter developed by the GNOME Project, Qt developed by the Qt Project and led by The Qt Company, and Enlightenment Foundation Libraries
The Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL) are a set of graphics libraries that grew out of the development of Enlightenment, a window manager and Wayland compositor. The project's focus is to make the EFL a flexible yet powerful and easy t ...
(EFL) developed primarily by the Enlightenment team.
* A package management system, such as dpkg and RPM. Alternatively packages can be compiled from binary or source tarballs.
* User interface programs such as command shells or windowing environments.
User interface
Theuser interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
, also known as the shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard outer layer of a marine ani ...
, is either a command-line interface (CLI), a graphical user interface (GUI), or controls attached to the associated hardware, which is common for embedded systems. For desktop systems, the default user interface is usually graphical, although the CLI is commonly available through terminal emulator
A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term ''terminal'' covers all remote term ...
windows or on a separate virtual console
The Virtual Console was a line of downloadable retro video games for Nintendo's Wii and Wii U home video game consoles and the Nintendo 3DS family of handheld systems. The Virtual Console lineup consisted of titles originally released on pa ...
.
CLI shells are text-based user interfaces, which use text for both input and output. The dominant shell used in Linux is the Bourne-Again Shell (bash), originally developed for the GNU Project; other shells such as Zsh are also used. Most low-level Linux components, including various parts of the userland, use the CLI exclusively. The CLI is particularly suited for automation of repetitive or delayed tasks and provides very simple inter-process communication
In computer science, interprocess communication (IPC) is the sharing of data between running Process (computing), processes in a computer system. Mechanisms for IPC may be provided by an operating system. Applications which use IPC are often cat ...
.

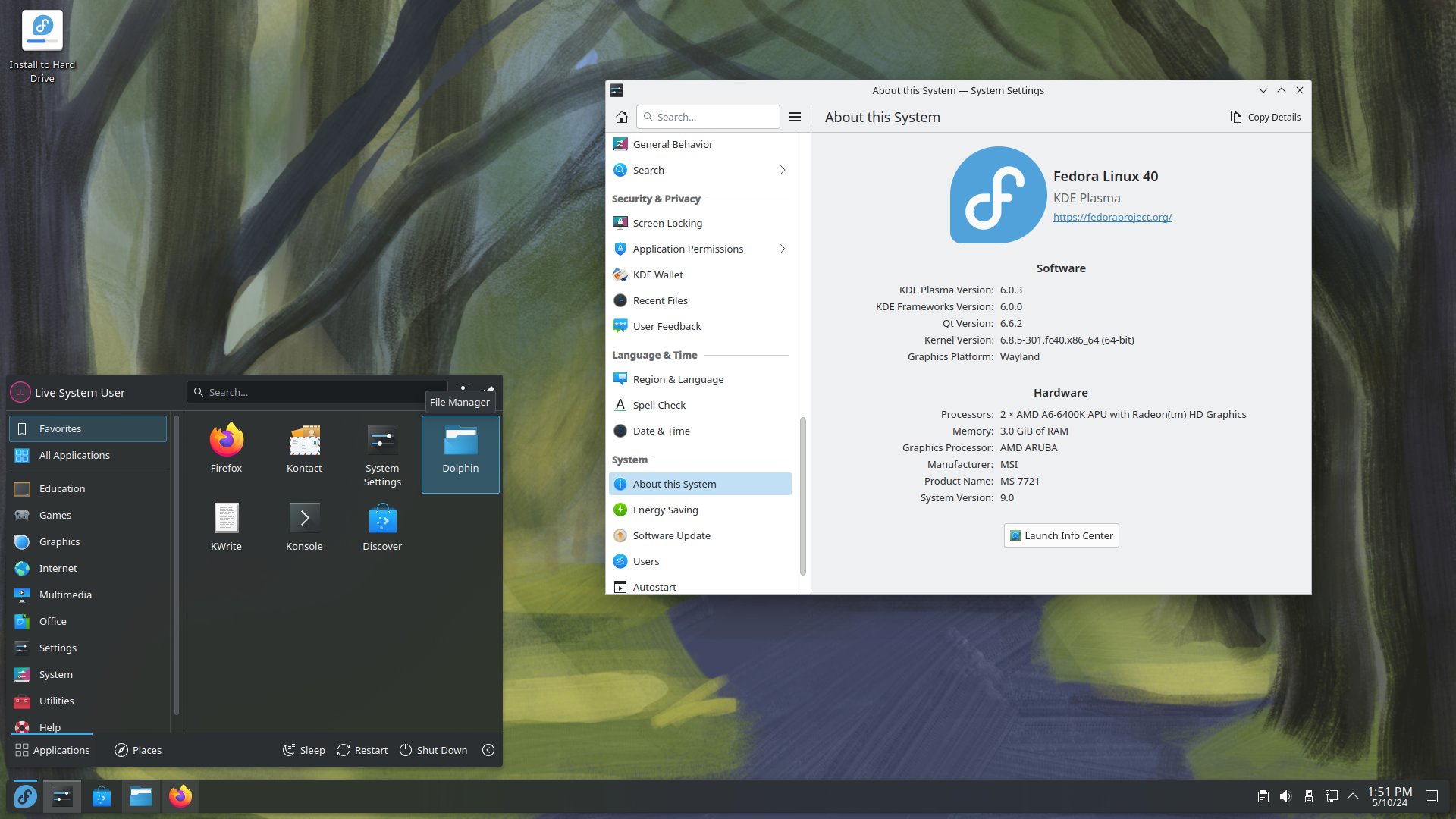 On desktop systems, the most popular user interfaces are the GUI shells, packaged together with extensive
On desktop systems, the most popular user interfaces are the GUI shells, packaged together with extensive desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphi ...
s, such as KDE Plasma
KDE Plasma is a Shell (computing), graphical shell developed by the KDE community for Unix-like operating systems. It serves as the interface layer between the user and the operating system, providing a graphical user interface (GUI) and workspa ...
, GNOME, MATE, Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
, LXDE, Pantheon, and Xfce, though a variety of additional user interfaces exist. Most popular user interfaces are based on the X Window System, often simply called "X" or "X11". It provides network transparency and permits a graphical application running on one system to be displayed on another where a user may interact with the application; however, certain extensions of the X Window System are not capable of working over the network. Several X display servers exist, with the reference implementation, X.Org Server, being the most popular. Several types of
Several types of window manager
A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of window (computing), windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They ...
s exist for X11, including tiling, dynamic, stacking, and compositing. Window managers provide means to control the placement and appearance of individual application windows, and interact with the X Window System. Simpler X window managers such as dwm, ratpoison, or i3wm provide a minimalist functionality, while more elaborate window managers such as FVWM, Enlightenment, or Window Maker provide more features such as a built-in taskbar and themes, but are still lightweight when compared to desktop environments. Desktop environments include window managers as part of their standard installations, such as Mutter (GNOME), KWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System and a Wayland (display server protocol)#Wayland compositors, Wayland compositor. It is released as a part of KDE Plasma, for which it is the default window manager. KWin can also be used on its o ...
(KDE), or Xfwm (xfce), although users may choose to use a different window manager if preferred.
Wayland is a display server protocol intended as a replacement for the X11 protocol; , it has received relatively wide adoption. Unlike X11, Wayland does not need an external window manager and compositing manager. Therefore, a Wayland compositor takes the role of the display server, window manager, and compositing manager. Weston is the reference implementation of Wayland, while GNOME's Mutter and KDE's KWin are being ported to Wayland as standalone display servers. Enlightenment has already been successfully ported since version 19. Additionally, many window managers have been made for Wayland, such as Sway or Hyprland, as well as other graphical utilities such as Waybar or Rofi.
Video input infrastructure
Linux currently has two modern kernel-userspace APIs for handling video input devices: V4L2 API for video streams and radio, and DVB API for digital TV reception. Due to the complexity and diversity of different devices, and due to the large number of formats and standards handled by those APIs, this infrastructure needs to evolve to better fit other devices. Also, a good userspace device library is the key to the success of having userspace applications to be able to work with all formats supported by those devices.Development
copyleft
Copyleft is the legal technique of granting certain freedoms over copies of copyrighted works with the requirement that the same rights be preserved in derivative works. In this sense, ''freedoms'' refers to the use of the work for any purpose, ...
, a kind of reciprocity: any work derived from a copyleft piece of software must also be copyleft itself. The most common free software license, the GNU General Public License (GPL), is a form of copyleft and is used for the Linux kernel and many of the components from the GNU Project.
Linux-based distributions are intended by developers for interoperability with other operating systems and established computing standards. Linux systems adhere to POSIX, Single UNIX Specification
The Single UNIX Specification (SUS) is a standard for computer operating systems, compliance with which is required to qualify for using the "UNIX" trademark. The standard specifies programming interfaces for the C language, a command-line shell, ...
(SUS), Linux Standard Base (LSB), ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
, and ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
standards where possible, although to date only one Linux distribution has been POSIX.1 certified, Linux-FT. The Open Group
The Open Group is a global consortium that seeks to "enable the achievement of business objectives" by developing " open, vendor-neutral technology standards and certifications." It has 900+ member organizations and provides a number of services ...
has tested and certified at least two Linux distributions as qualifying for the Unix trademark, EulerOS and Inspur K-UX.
Free software projects, although developed through collaboration
Collaboration (from Latin ''com-'' "with" + ''laborare'' "to labor", "to work") is the process of two or more people, entities or organizations working together to complete a task or achieve a goal. Collaboration is similar to cooperation. The ...
, are often produced independently of each other. The fact that the software licenses explicitly permit redistribution, however, provides a basis for larger-scale projects that collect the software produced by stand-alone projects and make it available all at once in the form of a Linux distribution.
Many Linux distributions manage a remote collection of system software and application software packages available for download and installation through a network connection. This allows users to adapt the operating system to their specific needs. Distributions are maintained by individuals, loose-knit teams, volunteer organizations, and commercial entities. A distribution is responsible for the default configuration of the installed Linux kernel, general system security, and more generally integration of the different software packages into a coherent whole. Distributions typically use a package manager such as apt, yum, zypper, pacman or portage to install, remove, and update all of a system's software from one central location.
Community
A distribution is largely driven by its developer and user communities. Some vendors develop and fund their distributions on a volunteer basis,Debian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
being a well-known example. Others maintain a community version of their commercial distributions, as Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
does with Fedora, and SUSE does with openSUSE.
In many cities and regions, local associations known as Linux User Groups (LUGs) seek to promote their preferred distribution and by extension free software. They hold meetings and provide free demonstrations, training, technical support, and operating system installation to new users. Many Internet communities also provide support to Linux users and developers. Most distributions and free software / open-source projects have IRC
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called '' channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat ...
chatrooms or newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start ...
s. Online forums are another means of support, with notable examples being Unix & Linux Stack Exchange, LinuxQuestions.org and the various distribution-specific support and community forums, such as ones for Ubuntu
Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed primarily of free and open-source software. Developed by the British company Canonical (company), Canonical and a community of contributors under a Meritocracy, meritocratic gover ...
, Fedora, Arch Linux, Gentoo, etc. Linux distributions host mailing list
A mailing list is a collection of names and addresses used by an individual or an organization to send material to multiple recipients.
Mailing lists are often rented or sold. If rented, the renter agrees to use the mailing list only at contra ...
s; commonly there will be a specific topic such as usage or development for a given list.
There are several technology websites with a Linux focus. Print magazines on Linux often bundle cover disks that carry software or even complete Linux distributions.
Although Linux distributions are generally available without charge, several large corporations sell, support, and contribute to the development of the components of the system and free software. An analysis of the Linux kernel in 2017 showed that well over 85% of the code was developed by programmers who are being paid for their work, leaving about 8.2% to unpaid developers and 4.1% unclassified. Some of the major corporations that provide contributions include Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
, Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
, Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, AMD, Oracle
An oracle is a person or thing considered to provide insight, wise counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. If done through occultic means, it is a form of divination.
Descript ...
, and Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
. Several corporations, notably Red Hat, Canonical, and SUSE have built a significant business around Linux distributions.
The free software licenses, on which the various software packages of a distribution built on the Linux kernel are based, explicitly accommodate and encourage commercialization; the relationship between a Linux distribution as a whole and individual vendors may be seen as symbiotic
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biolo ...
. One common business model
A business model describes how a Company, business organization creates, delivers, and captures value creation, value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-pub ...
of commercial suppliers is charging for support, especially for business users. A number of companies also offer a specialized business version of their distribution, which adds proprietary support packages and tools to administer higher numbers of installations or to simplify administrative tasks.
Another business model is to give away the software to sell hardware. This used to be the norm in the computer industry, with operating systems such as CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
, Apple DOS, and versions of the classic Mac OS
Mac OS (originally System Software; retronym: Classic Mac OS) is the series of operating systems developed for the Mac (computer), Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and end ...
before 7.6 freely copyable (but not modifiable). As computer hardware standardized throughout the 1980s, it became more difficult for hardware manufacturers to profit from this tactic, as the OS would run on any manufacturer's computer that shared the same architecture.
Programming on Linux
Mostprogramming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s support Linux either directly or through third-party community based ports Ports collections (or ports trees, or just ports) are the sets of makefiles and Patch (Unix), patches provided by the BSD-based operating systems, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD, as a simple method of installing software or creating binary packages. T ...
. The original development tools used for building both Linux applications and operating system programs are found within the GNU toolchain, which includes the GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a collection of compilers from the GNU Project that support various programming languages, Computer architecture, hardware architectures, and operating systems. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) distributes ...
(GCC) and the GNU Build System. Amongst others, GCC provides compilers for Ada, C, C++, Go and Fortran. Many programming languages have a cross-platform reference implementation that supports Linux, for example PHP, Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language".
Perl was developed ...
, Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapph ...
, Python, Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, Go, Rust and Haskell
Haskell () is a general-purpose, statically typed, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language ...
. First released in 2003, the LLVM
LLVM, also called LLVM Core, is a target-independent optimizer and code generator. It can be used to develop a Compiler#Front end, frontend for any programming language and a Compiler#Back end, backend for any instruction set architecture. LLVM i ...
project provides an alternative cross-platform open-source compiler for many languages. Proprietary compilers for Linux include the Intel C++ Compiler, Sun Studio, and IBM XL C/C++ Compiler. BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
is available in procedural form from QB64, PureBasic, Yabasic, GLBasic, Basic4GL, XBasic, wxBasic, SdlBasic, and Basic-256, as well as object oriented through Gambas, FreeBASIC
FreeBASIC is a FOSS, free and open source multiplatform compiler and programming language based on BASIC licensed under the GNU General Public License, GNU GPL for Microsoft Windows, protected-mode MS-DOS (DOS extender), Linux, FreeBSD and Xbox ...
, B4X, Basic for Qt, Phoenix Object Basic, NS Basic, ProvideX, Chipmunk Basic, RapidQ and Xojo. Pascal is implemented through GNU Pascal
GNU Pascal (GPC) is a Pascal programming language, Pascal compiler composed of a frontend to GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), similar to the way Fortran and other languages were added to GCC. GNU Pascal is International Organization for Standardizat ...
, Free Pascal, and Virtual Pascal, as well as graphically via Lazarus, PascalABC.NET, or Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
using FireMonkey
FireMonkey (abbreviated FMX) is a cross-platform GUI framework developed by Embarcadero Technologies for use in Delphi, C++Builder oPython using Object Pascal, C++ or Python to build cross-platform applications for Windows, macOS, iOS, and ...
(previously through Borland Kylix).
A common feature of Unix-like systems, Linux includes traditional specific-purpose programming languages targeted at scripting, text processing and system configuration and management in general. Linux distributions support shell scripts, awk, sed and make. Many programs also have an embedded programming language to support configuring or programming themselves. For example, regular expression
A regular expression (shortened as regex or regexp), sometimes referred to as rational expression, is a sequence of characters that specifies a match pattern in text. Usually such patterns are used by string-searching algorithms for "find" ...
s are supported in programs like grep and locate, the traditional Unix message transfer agent Sendmail contains its own Turing complete scripting system, and the advanced text editor GNU Emacs
GNU Emacs is a text editor and suite of free software tools. Its development began in 1984 by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU ...
is built around a general purpose Lisp
Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized Polish notation#Explanation, prefix notation.
Originally specified in the late 1950s, ...
interpreter.
Most distributions also include support for PHP, Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language".
Perl was developed ...
, Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapph ...
, Python and other dynamic languages. While not as common, Linux also supports C# and other CLI languages
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is ch ...
(via Mono), Vala, and Scheme. Guile Scheme acts as an extension language targeting the GNU system utilities, seeking to make the conventionally small, static, compiled C programs of Unix design rapidly and dynamically extensible via an elegant, functional high-level scripting system; many GNU programs can be compiled with optional Guile bindings to this end. A number of Java virtual machine
A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally descr ...
s and development kits run on Linux, including the original Sun Microsystems JVM ( HotSpot), and IBM's J2SE RE, as well as many open-source projects like Kaffe and Jikes RVM; Kotlin, Scala, Groovy
''Groovy'' (or, less commonly, ''groovie'' or ''groovey'') is a slang colloquialism popular during the 1960s and 1970s. It is roughly synonymous with words such as "excellent", "fashionable", or "amazing", depending on context.
History
The word ...
and other JVM languages are also available.
GNOME and KDE
KDE is an international free software community that develops free and open-source software. As a central development hub, it provides tools and resources that enable collaborative work on its projects. Its products include the KDE Plasma gra ...
are popular desktop environments and provide a framework for developing applications. These projects are based on the GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
and Qt widget toolkits, respectively, which can also be used independently of the larger framework. Both support a wide variety of languages. There are a number of Integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
s available including Anjuta, Code::Blocks, CodeLite, Eclipse, Geany, ActiveState Komodo, KDevelop, Lazarus, MonoDevelop, NetBeans
NetBeans is an integrated development environment (IDE) for Java (programming language), Java. NetBeans allows applications to be developed from a set of modular software components called ''modules''. NetBeans runs on Microsoft Windows, Windows, ...
, and Qt Creator
Qt Creator is a cross-platform C++, JavaScript, Python and QML integrated development environment (IDE) which simplifies GUI application development. It is part of the SDK for the Qt GUI application development framework and uses the Q ...
, while the long-established editors Vim, nano and Emacs
Emacs (), originally named EMACS (an acronym for "Editor Macros"), is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, s ...
remain popular.
Hardware support
Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit computing, 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-b ...
or Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also the f ...
16-bit microprocessors, while the μClinux kernel fork may run on systems without a memory management unit
A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit that examines all references to computer memory, memory, and translates the memory addresses being referenced, known as virtual mem ...
. The kernel also runs on architectures that were only ever intended to use a proprietary manufacturer-created operating system, such as Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
computers (with PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
, and Apple silicon
Apple silicon is a series of system on a chip (SoC) and system in a package (SiP) processors designed by Apple Inc., mainly using the ARM architecture family, ARM architecture. They are used in nearly all of the company's devices including Mac ...
processors), PDAs, video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s, portable music players, and mobile phones.
Linux has a reputation for supporting old hardware very well by maintaining standardized drivers for a long time. There are several industry associations and hardware conferences devoted to maintaining and improving support for diverse hardware under Linux, such as FreedomHEC. Over time, support for different hardware has improved in Linux, resulting in any off-the-shelf purchase having a "good chance" of being compatible.
In 2014, a new initiative was launched to automatically collect a database of all tested hardware configurations.
Uses
Market share and uptake
Many quantitative studies of free/open-source software focus on topics including market share and reliability, with numerous studies specifically examining Linux. The Linux market is growing, and the Linux operating system market size is expected to see a growth of 19.2% by 2027, reaching $15.64 billion, compared to $3.89 billion in 2019. Analysts project a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.7% between 2024 and 2032, culminating in a market size of US$34.90 billion by the latter year. Analysts and proponents attribute the relative success of Linux to its security, reliability, low cost, and freedom fromvendor lock-in
In economics, vendor lock-in, also known as proprietary lock-in or customer lockin, makes a customer dependent on a vendor for products, unable to use another vendor without substantial switching costs.
The use of open standards and alternati ...
.
; Desktops and laptops
: According to web server statistics (that is, based on the numbers recorded from visits to websites by client devices), in October 2024, the estimated market share of Linux on desktop computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuratio ...
s was around 4.3%. In comparison, Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
had a market share of around 73.4%, while macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
covered around 15.5%.
; Web servers
: W3Cook publishes stats that use the top 1,000,000 Alexa domains, which estimate that 96.55% of web servers run Linux, 1.73% run Windows, and 1.72% run FreeBSD.
:W3Techs publishes stats that use the top 10,000,000 Alexa domains and the top 1,000,000 Tranco domains, updated monthly and estimate that Linux is used by 39% of the web servers, versus 21.9% being used by Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
. 40.1% used other types of Unix.
: IDC's Q1 2007 report indicated that Linux held 12.7% of the overall server market at that time; this estimate was based on the number of Linux servers sold by various companies, and did not include server hardware purchased separately that had Linux installed on it later.
As of 2024, estimates suggest Linux accounts for at least 80% of the public cloud workload, partly thanks to its widespread use in platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.ZDNet report that 96.3% of the top one million web servers are running Linux. W3Techs state that Linux powers at least 39.2% of websites whose operating system is known, with other estimates saying 55%.; Mobile devices : Android, which is based on the Linux kernel, has become the dominant operating system for smartphones. In April 2023, 68.61% of mobile devices accessing websites using StatCounter were from Android. Android is also a popular operating system for tablets, being responsible for more than 60% of tablet sales . According to web server statistics, Android has a market share of about 71%, with iOS holding 28%, and the remaining 1% attributed to various niche platforms. ; Film production : For years, Linux has been the platform of choice in the film industry. The first major film produced on Linux servers was 1997's '' Titanic''. Since then major studios including
DreamWorks Animation
DreamWorks Animation LLC (DWA, also known as DreamWorks Animation Studios or simply DreamWorks) is an American animation studio, owned by Comcast's NBCUniversal as part of Universal Pictures, a division of Universal Studios, Inc, Universal Stud ...
, Pixar, Weta Digital, and Industrial Light & Magic have migrated to Linux. According to the Linux Movies Group, more than 95% of the servers and desktops at large animation and visual effects companies use Linux.
; Use in government
: Linux distributions have also gained popularity with various local and national governments. News of the Russian military creating its own Linux distribution has also surfaced, and has come to fruition as the G.H.ost Project. The Indian state of Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
has gone to the extent of mandating that all state high schools run Linux on their computers. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
uses Linux exclusively as the operating system for its Loongson processor family to achieve technology independence. In Spain, some regions have developed their own Linux distributions, which are widely used in education and official institutions, like gnuLinEx in Extremadura and Guadalinex in Andalusia. France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
have also taken steps toward the adoption of Linux. North Korea's Red Star OS, developed , is based on a version of Fedora Linux.
Copyright, trademark, and naming
The Linux kernel is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2. The GPL requires that anyone who distributes software based on source code under this license must make the originating source code (and any modifications) available to the recipient under the same terms. Other key components of a typical Linux distribution are also mainly licensed under the GPL, but they may use other licenses; many libraries use the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), a more permissive variant of the GPL, and the X.Org implementation of the X Window System uses theMIT License
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility.
Unl ...
.
Torvalds states that the Linux kernel will not move from version 2 of the GPL to version 3. He specifically dislikes some provisions in the new license which prohibit the use of the software in digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures, such as access control technologies, can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted works. DRM ...
. It would also be impractical to obtain permission from all the copyright holders, who number in the thousands.
A 2001 study of Red Hat Linux 7.1 found that this distribution contained 30 million source lines of code. Using the Constructive Cost Model, the study estimated that this distribution required about eight thousand person-years of development time. According to the study, if all this software had been developed by conventional proprietary means, it would have cost about to develop in in the United States. Most of the source code (71%) was written in the C programming language, but many other languages were used, including C++, Lisp
Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized Polish notation#Explanation, prefix notation.
Originally specified in the late 1950s, ...
, assembly language, Perl, Python, Fortran, and various shell scripting languages. Slightly over half of all lines of code were licensed under the GPL. The Linux kernel itself was 2.4 million lines of code, or 8% of the total.
In a later study, the same analysis was performed for Debian version 4.0 (etch, which was released in 2007). This distribution contained close to 283 million source lines of code, and the study estimated that it would have required about seventy three thousand man-years and cost (in dollars) to develop by conventional means.
 In the United States, the name ''Linux'' is a trademark registered to Linus Torvalds. Initially, nobody registered it. However, on August 15, 1994, William R. Della Croce Jr. filed for the trademark ''Linux'', and then demanded royalties from Linux distributors. In 1996, Torvalds and some affected organizations sued him to have the trademark assigned to Torvalds, and, in 1997, the case was settled. The licensing of the trademark has since been handled by the Linux Mark Institute (LMI). Torvalds has stated that he trademarked the name only to prevent someone else from using it. LMI originally charged a nominal sublicensing fee for use of the Linux name as part of trademarks, but later changed this in favor of offering a free, perpetual worldwide sublicense.
In the United States, the name ''Linux'' is a trademark registered to Linus Torvalds. Initially, nobody registered it. However, on August 15, 1994, William R. Della Croce Jr. filed for the trademark ''Linux'', and then demanded royalties from Linux distributors. In 1996, Torvalds and some affected organizations sued him to have the trademark assigned to Torvalds, and, in 1997, the case was settled. The licensing of the trademark has since been handled by the Linux Mark Institute (LMI). Torvalds has stated that he trademarked the name only to prevent someone else from using it. LMI originally charged a nominal sublicensing fee for use of the Linux name as part of trademarks, but later changed this in favor of offering a free, perpetual worldwide sublicense.
Richard Stallman
Richard Matthew Stallman ( ; born March 16, 1953), also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to ...
, president of the FSF. The foundation explicitly takes no issue over the name Android for the Android OS, which is also an operating system based on the Linux kernel, as GNU is not a part of it.
A minority of public figures and software projects other than Stallman and the FSF, notably distributions consisting of only free software, such as Debian (which had been sponsored by the FSF up to 1996), also use ''GNU/Linux'' when referring to the operating system as a whole. Most media and common usage, however, refers to this family of operating systems simply as ''Linux'', as do many large Linux distributions (for example, SUSE Linux and Red Hat Enterprise Linux).
, about 8% to 13% of the lines of code of the Linux distribution Ubuntu (version "Natty") is made of GNU components (the range depending on whether GNOME is considered part of GNU); meanwhile, 6% is taken by the Linux kernel, increased to 9% when including its direct dependencies. ( self-published data)
See also
*Comparison of Linux distributions
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organizational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, includi ...
* Comparison of open-source and closed-source software
* Comparison of operating systems
* Comparison of X Window System desktop environments
* Criticism of desktop Linux
* Criticism of Linux
* Linux kernel version history
This article documents the version history of the Linux kernel.
Each major version identified by the first two numbers of a release version is designated one of the following levels of support:
* Supported until next stable version and 3 mont ...
* Linux Documentation Project
* Linux From Scratch
* Linux Software Map
Linux Software Map (LSM) is a standard text file format for describing Linux software. It also refers to the database constructed from these files. LSM is one of the standard methods for announcing a new software release for Linux.
File forma ...
* List of Linux distributions
* List of games released on Linux
* List of operating systems
* Loadable kernel module
* Usage share of operating systems
* Timeline of operating systems
Notes
References
External links
* (archived)Linux kernel website and archives
The History of Linux in GIT Repository Format 1992–2010
(archived) {{Authority control 1991 software Computing platforms Cross-platform software Finnish inventions Free software programmed in C Linus Torvalds Operating systems Unix variants Open source projects